What are Hives?
Hives are raised red bumps (welts) or splotches on the skin that are usually very itchy. They are a type of swelling on the surface of your skin that happen when your body has an allergic reaction to something.
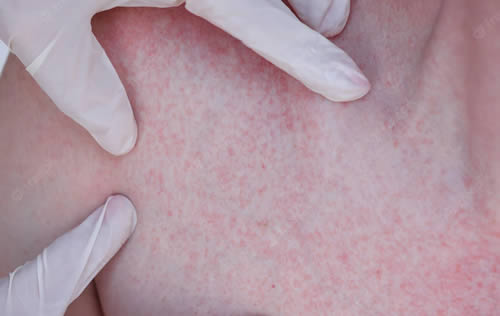
What are the signs and symptoms of Hives?
Individual hives can take from 30 minutes to 36 hours to disappear. Chronic hives, referred to as urticaria, last longer than six weeks to go away, but frequently reoccur. If swelling occurs below the surface of the skin, a condition called angioedema, you should seek medical attention because angioedema can affect the internal organs.
Signs of hives include:
- Developing in batches
- Often raised
- Small, round rings or large patches with a red flare
- Usually itch
What are the causes of Hives?
Hives develop when mast cells release histamine and other chemicals into your bloodstream, causing small blood vessels to leak. Generally, hives are an allergic reaction to a food, animal or medication. Sun exposure, stress, excessive perspiration and other more serious conditions, like lupus, can bring on hives.
What treatments are available at the dermatologist for Hives?
Our dermatologist may recommend various treatments and strategies to help manage and alleviate hives, depending on the severity and underlying causes.
Here are some common treatments available at the dermatologist’s office:
- Antihistamines: Non-prescription (over-the-counter) antihistamines like cetirizine (Zyrtec), loratadine (Claritin), or fexofenadine (Allegra) can help relieve itching and reduce the severity of hives. Dermatologists may also prescribe stronger prescription antihistamines.
- Corticosteroids: Topical corticosteroid creams or ointments can be applied directly to the affected skin to reduce inflammation and itching. Oral corticosteroids may be prescribed for severe cases of hives or when topical treatments are not effective.
- Epinephrine (EpiPen): In rare cases of severe hives accompanied by anaphylaxis or difficulty breathing, an epinephrine auto-injector (EpiPen) may be prescribed to quickly relieve symptoms.
- Immune-suppressing medications: For chronic or severe cases of hives that do not respond to other treatments, dermatologists may prescribe medications that suppress the immune system, such as cyclosporine or omalizumab (Xolair).
- Triggers identification and avoidance: Dermatologists may work with patients to identify and avoid triggers that can exacerbate hives. Common triggers include certain foods, medications, insect stings, physical stimuli (like heat, cold, or pressure), and stress.
- Physical therapies: For certain types of hives, such as cold urticaria or pressure urticaria, dermatologists may recommend physical therapies like cold packs or pressure-reducing strategies to manage symptoms.
- Allergy testing: If an allergic trigger is suspected, allergen testing may be conducted to identify specific allergens responsible for hives. This can help with avoidance strategies.

FAQ About Hives
Are hives contagious?
Hives are not contagious and cannot be spread from person to person through direct contact.
How long do hives last?
Hives can last anywhere from a few minutes to several days or even weeks. They can be chronic, or recurring, in some cases.
Can hives lead to more serious conditions?
In some cases, hives can be a symptom of a more serious allergic reaction, such as anaphylaxis. If hives are accompanied by difficulty breathing, swelling of the face or throat, or a rapid heartbeat, it is important to seek immediate medical attention.
Is there a dermatologist near me in Saint Paul that offers treatment for hives?
Yes. At our Saint Paul dermatology office we offer treatment for hives to patients from Saint Paul and the surrounding area. Contact our office today to schedule an appointment.

